Database User Management Automation
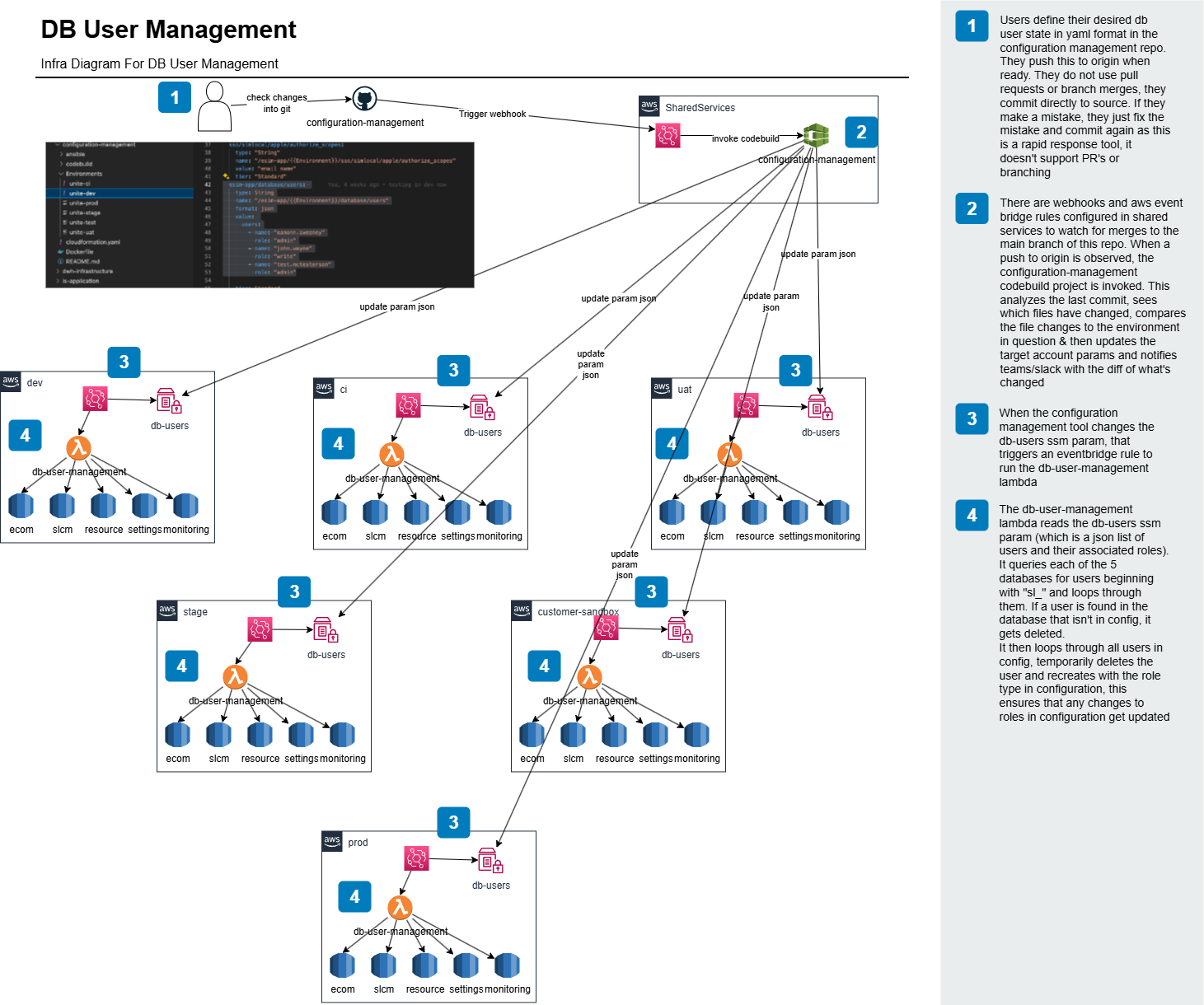
Automated database user management system that handles user permissions across multiple RDS Aurora clusters and AWS accounts using Lambda functions,[...]

Automated database user management system that handles user permissions across multiple RDS Aurora clusters and AWS accounts using Lambda functions, EventBridge, and MySQL automation.
Table of Contents
Project Overview
Managing database user permissions manually across multiple RDS clusters becomes complex and error-prone as organizations scale. This project implements an automated solution that manages database users, permissions, and access control across multiple Aurora MySQL clusters and AWS accounts.
Architecture
The solution leverages several AWS services:
| Technology | Purpose |
| AWS Lambda | Executes logic |
| AWS EventBridge | Watches for event changes |
| AWS RDS Aurora | Hosts the databases |
| AWS Parameter Store | Stores overall configuration |
| AWS Secrets Manager | Stores admin database credentials for management |
| AWS IAM | AWS Resource permissions |
| Python Boto3 | AWS API Interactions |
| MySQL | Database actions |
Key Features
Automated User Lifecycle Management
| Non Functional Requirement | Description |
| User Creation | The tool is idempotent |
| Permission Assignment | The tool will assign appropriate role based permissions from configuration. This includes downgrading permissions as well as elevating them |
| User Deactivation | If a user isn't in configuration when the tool is run, it should remove the user |
Multi-Account Support
- Cross-account user management
- Centralized control plane
- Consistent user naming conventions
Security and Compliance
- Least-privilege access principles
- Audit logging of all user operations
- Centralized SSO based authentication
- Role-based permission inheritance
Implementation Details
Event-Driven Architecture
The system responds to updates to SSM Parameter store updates.
Lambda Function Design
The core Lambda function handles:
- Reading json configuration for all users in SSM Parameter Store
- Connecting to each database in it's account
- Listing all users with specified naming convention
- Comparing configuration to database status
- Adding/Deleting/Modifying state in DB's according to configuration
Database Connection Management
def connect_to_database(db_connection_data: dict) -> mysql.connector.connect:
"""
Connect to the target database
Parameters:
db_connection_data (dict): The connection data for the target database
db_connection_data.host = string
db_connection_data.user = string
db_connection_data.pass = string
db_connection_data.name = string
"""
try:
connection = mysql.connector.connect(
host=db_connection_data['host'],
user=db_connection_data['user'],
password=db_connection_data['pass'],
database=db_connection_data['name']
)
logger.info(f"DB CONNECTION: {connection}")
return connection
except mysql.connector.Error as e:
logger.error(f"ERROR: Unexpected error: Could not connect to Serverless {db_connection_data['db_name']} MySQL instance.")
logger.error(e)
sys.exit()def get_secret_value(secret_arn: str, json_key: str) -> str:
"""
Get a secret value from AWS Secrets Manager
parameters:
secret_arn (str): The ARN of the secret in Secrets Manager
json_key (str): The key in the JSON object to retrieve
returns:
str: The value of the key in the JSON object
"""
logger.info(f'Getting secret value for {secret_arn}, key: {json_key}')
try:
response = sm_client.get_secret_value(
SecretId=secret_arn
)
raw_secret = response.get('SecretString')
secret_json = json.loads(raw_secret)
return secret_json[json_key]
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"ERROR: Unexpected error: Could not retrieve for {secret_arn}. Maybe the key {json_key} does not exist.")
logger.error(e)
sys.exit()User Management
The function below manages user creation and permissions:
def create_db_user(db_connection_data: dict, user_details: dict) -> None:
"""
Creates a database user and enforces the permissions on the role passed
This will support downgrading and upgrading a user's role
Parameters:
db_connection_data (dict): The connection data for the target database
db_connection_data.host = string
db_connection_data.user = string
db_connection_data.pass = string
db_connection_data.name = string
user_details (dict): The user details, including the name and role
user_details.name = string
user_details.role = string (allowed values: read, write, admin, trusted_admin)
"""
# Define the permissions for each role
permissions = {
'read': 'SELECT',
'write': 'SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE',
'admin': 'SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, REFERENCES, INDEX, ALTER, CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES, CREATE VIEW, SHOW VIEW, CREATE ROUTINE, ALTER ROUTINE, EXECUTE, EVENT, TRIGGER',
'trusted_admin': 'ALL PRIVILEGES'
}
conn = connect_to_database(db_connection_data=db_connection_data)
create_user_result = execute_sql(f"CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS 'sl_{user_details['name']}'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH AWSAuthenticationPlugin as 'RDS';", conn)
logger.info(f"Create User Result: {create_user_result}")
revoke_permissions_result = execute_sql(f"REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES, GRANT OPTION FROM 'sl_{user_details['name']}'@'%';", conn)
logger.info(f"Revoke Permissions Result: {revoke_permissions_result}")
grant_permissions_result = execute_sql(f"GRANT {permissions.get(user_details['role'])} ON {db_connection_data['name']}.* TO 'sl_{user_details['name']}'@'%';", conn)
logger.info(f"Grant Permissions Result: {grant_permissions_result}")
conn.close()The function below will delete users:
def delete_db_users(db_connection_data: dict, user_name: str) -> None:
"""
Deletes a database user, if they don't exist, it's fine
"""
logger.info(f"About to Connect to {db_connection_data['name']} in order to delete {user_name}")
conn = connect_to_database(db_connection_data=db_connection_data)
drop_user_result = execute_sql(f"DROP USER IF EXISTS '{user_name}'@'%';", conn)
logger.info(f"Drop User Result: {drop_user_result}")
conn.close()The handler below is called whenever the ssm parameter where configuration is stored is changed:
def handler(event, context):
"""
Lambda handler function
- Gets list of database users from SSM
- Loops through each database
- Gets the target db connection data (querying RDS for endpoint and secrets manager arn, then gets the secret value)
- Gets the list of existing users in the database
- Finds which users aren't in config and deletes them
- Goes through the users in config and ensures they're created (removes permissions for each and then reapplies permissions)
"""
# Make sure we're logging correctly
configure_logging()
# Get the configuration users from SSM
db_users = get_ssm_value(f'/{Environment}/database/users')
logger.info(f"DB users from configuration: {db_users}")
# Define the list of databases we want to manage
databases = ['db1', 'db2', 'db3', 'db4', 'db5']
# Loop through each database
for db in databases:
#Get the target db connection data. This will return endpoint, username, password, port in a dict
target_db_connection_data = get_target_db_connection_data(db)
# Get the list of existing users in the database (we may want to delete some)
existing_users = list_db_users(target_db_connection_data)
# Find which users aren't in config and go delete them
for deletion_candidate in existing_users:
# Remove prefix from the username
deletion_candidate_user_name = deletion_candidate.get('User').removeprefix("sl_")
# Is the existing db user in the list taken from ssm?
delete_candidate = any(user.get("name") == deletion_candidate_user_name for user in db_users["users"])
# If not in config, we should delete
if delete_candidate:
logger.info(f"sl_{deletion_candidate_user_name} is in config, leave them be")
else:
logger.info(f"sl_{deletion_candidate_user_name} isn't in config, I should delete them here")
delete_db_users(target_db_connection_data, f"sl_{deletion_candidate_user_name}")
# Go through the users in config and ensure they're created
for user in db_users.get('users'):
logger.info(f"Creating: {user}")
create_db_user(target_db_connection_data, user)
Technical Implementation
Cross-Account Access
The system uses cross-account IAM roles to manage users across multiple AWS accounts:
- Central management account assumes roles in target accounts
- Target account roles have necessary RDS permissions
- Database operations performed with Secrets Manager managed role credentials
- Audit trail maintained in central logging account (if using control tower + an audit account)
Database User Naming Convention
Users follow a consistent naming pattern: ```<company-prefix>_<username> ```
This ensures:
- Easy identification of user origin
- No naming conflicts across non-managed accounts
Error Handling and Monitoring
- Comprehensive error logging
- CloudWatch metrics for operational visibility
- SNS notifications for critical failures
IAM Permissions
The below IAM permissions, will allow users to use the AWS CLI to call generate rds credentials using the cli command below
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Statement1",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"rds-db:connect"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:rds-db:eu-west-1:${AWS::AccountId}:dbuser:<db1_arn>/sl_${aws:PrincipalTag/UserName}",
"arn:aws:rds-db:eu-west-1:${AWS::AccountId}:dbuser:<db2_arn>/sl_${aws:PrincipalTag/UserName}",
"arn:aws:rds-db:eu-west-1:${AWS::AccountId}:dbuser:<db3_arn>/sl_${aws:PrincipalTag/UserName}",
"arn:aws:rds-db:eu-west-1:${AWS::AccountId}:dbuser:<db4_arn>/sl_${aws:PrincipalTag/UserName}",
"arn:aws:rds-db:eu-west-1:${AWS::AccountId}:dbuser:<db5_arn>/sl_${aws:PrincipalTag/UserName}",
]
}
]
}Remember to replace <db_arn> with the db arn of your rds cluster/instance and replace sl_ with your prefix
aws rds generate-db-auth-token --hostname <HOSTNAME> --port 3306 --username sl_<SSO_USERNAME>Connecting to databases
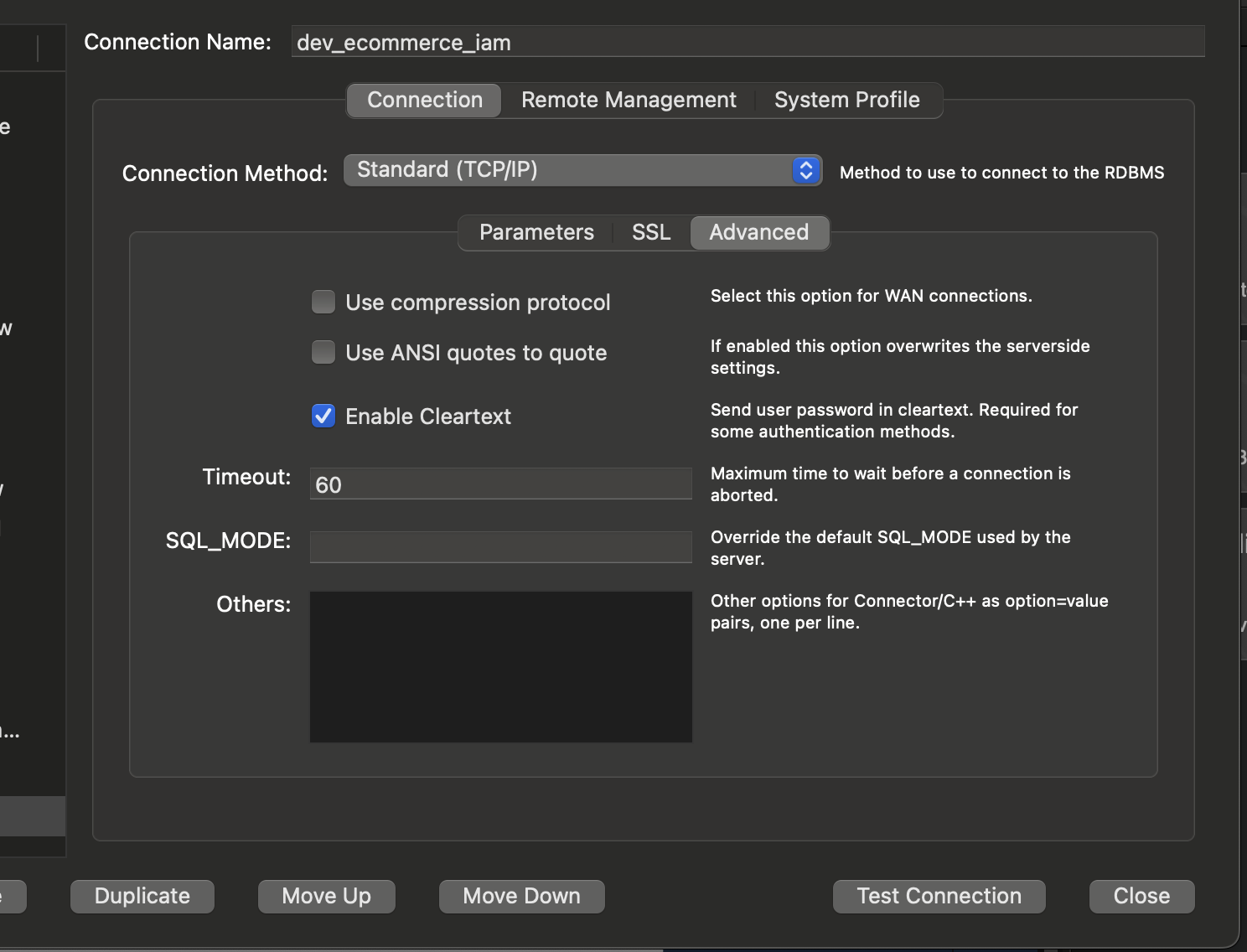
Configure your MySQL Client:
- MySQL Workbench
- Add New Connection
- ConnectionName: <env>_<db_name>_iam
- Hostname: <rds_endpoint>
- Username: sl_<sso_username>
- Password: <output from generate-db-auth-token command>
- Click on Advanced tab and ensure "Enable Cleartext" is ticked
- DBeaver
- File -> New -> Database connection -> MySQL
- Connection settings -> Main
- Connect By:
Host - Server Host: <rds_endpoint>
- Port: 3306
- Username: sl_<sso_username>
- Password: <output from generate-db-auth-token command>
- Connect By:
- Connection settings -> Driver properties
defaultAuthenticationPlugin:mysql_clear_password
- Connection settings -> SSL
- Use SSL: Check
- Verify server certificate: Uncheck
- Connection Settings -> Initialization -> Bootstrap Queries: add
SET SESSION max_execution_time = 300000;(enforces 5 minute timeout limit on all queries)
- JetBrains DataGrip
- Add New Data Source
- Name: <env>_<db_name>_iam
- Select Drivers tab & select the
Aurora MySQL (AWS driver) - General Settings
- Host: <rds endpoint>
- Authentication: User & Password
- User: sl_<sso_username>
- Password: <output from generate-db-auth-token command>
- Database: <database_name>
- Click the Advanced Tab
- authenticationPlugin:
com.mysql.cj.protocol.a.authentication.MysqlClearPasswordPlugin - VM environment: LIBMYSQL_ENABLE_CLEARTEXT_PLUGIN=1
- authenticationPlugin:
- Add New Data Source
Results and Impact
Operational Benefits
- Massive reduction in effort in manual database user management tasks
- Consistent permissions across all database clusters
- Centralized password management (sso + mfa)
Security Improvements
- Eliminated shared database accounts
- Implemented least-privilege access
- Automated access removal for departed employees
- Complete audit trail of database access changes
Scalability
- Supports unlimited RDS clusters
- Handles multiple AWS accounts seamlessly
- Scales with minimal effort
- Minimal infrastructure maintenance required