Multi-Account Configuration Management In AWS
This project page outlines a time when I designed and implemented a time-efficient, consistent way of managing SSM Parameter Store[...]

This project page outlines a time when I designed and implemented a time-efficient, consistent way of managing SSM Parameter Store configuration across multiple AWS accounts. The solution enforces state from source control and includes notification of updates to Slack.
There are many other tools that you can use to keep configuration central (like CloudMap) but in this case, configuration had already been decentralized and was heavily engrained in the organizations tech. Consistent configuration changes were becoming a problem for people within the organization and this solution improved the situation.
Table of Contents
Project Overview
Managing application configuration across multiple AWS accounts can be complex and error-prone. This project implements a GitOps-driven solution that automates configuration management using AWS SSM Parameter Store, ensuring consistency and auditability across many environments.
Architecture
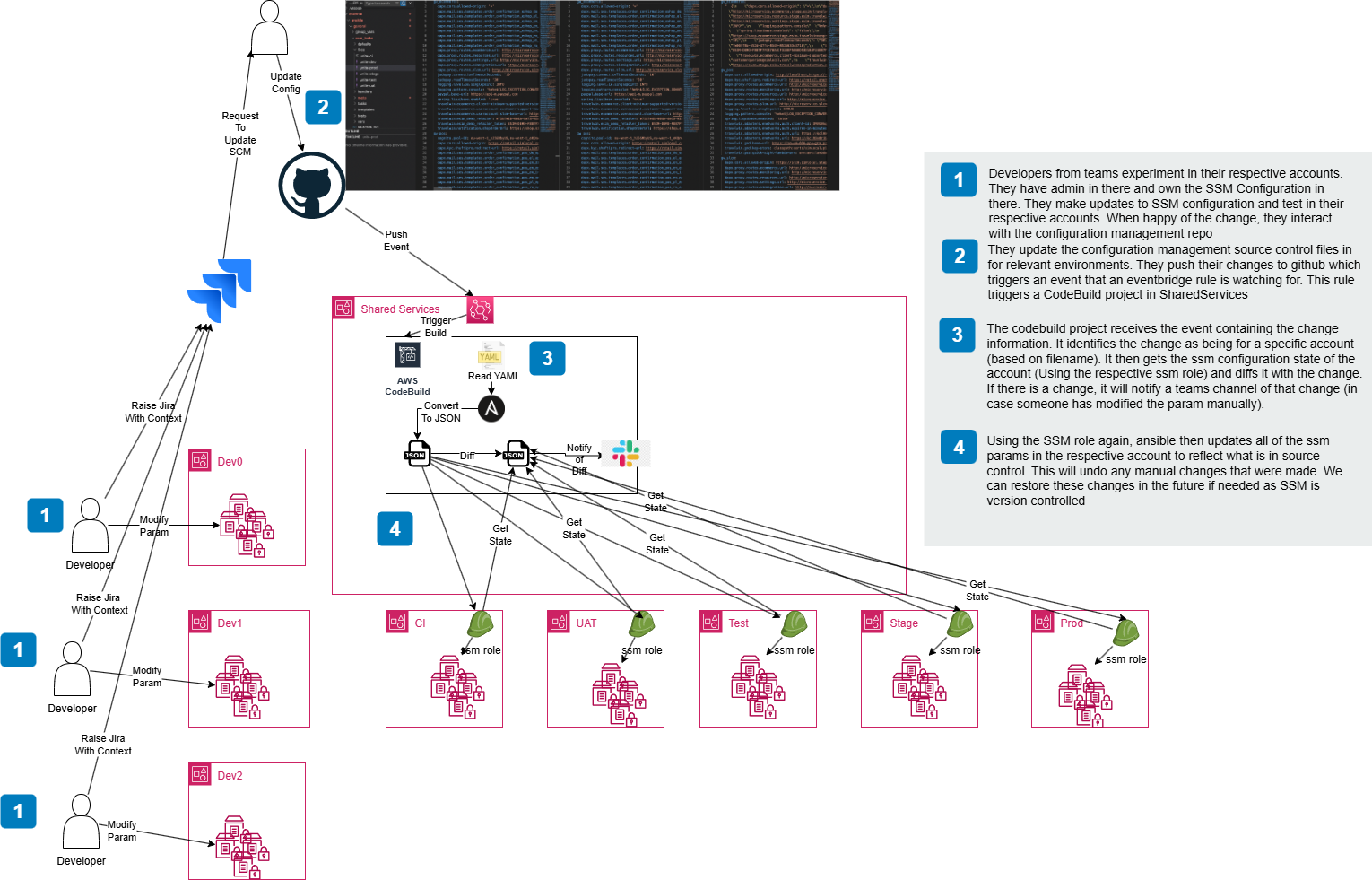
The solution leverages:
| Service | Function |
| AWS CodeBuild | Runtime |
| AWS SSM Parameter Store | Configuration Storage |
| GitOps | Workflow style of making operational changes through git |
| Ansible | Handles yaml conversion to json, reading ssm parameters and enforcing state from git |
| GitHub | Version Control provider |
Key Features
Automated Configuration Deployment
Configuration changes are automatically deployed across environments through GitOps workflows:
- Developers commit configuration changes to Git
- Github webhooks then trigger CodeBuild
- CodeBuild validates configuration format
- Ansible playbooks enforce ssm parameter state based on changes in the git commit
- SSM Parameter Store securely stores values
Implementation Benefits
Operational Efficiency & Consistency
- Configuration is pushed centrally so making changes to multiple accounts is simplified compared to manual updates (logging into multiple accounts, navigating to ssm parameter store, making manual updates)
- Rollback is simplified by using git to revert commits
- Configuration is committed in yaml, then converted to json, which ensures syntactical errors won't be committed to SSM(Ansible will error if there are)
Technical Implementation
The solution consists of several key components:
GitOps Workflow
Configuration is stored in Git repositories with environment-specific branches. Changes trigger automated pipelines that validate, test, and deploy configurations to the appropriate AWS accounts.
Ansible Automation
Ansible playbooks handle the deployment logic, including:
- Parameter validation and formatting
- Cross-account role assumption
- Batch parameter updates
- Slack notifications
SSM Parameter Store Structure
Parameters are organized in a hierarchical structure:
/application/{environment}/{service}/{parameter-name}
This structure enables:
- Easy parameter discovery
- Environment-specific overrides
- Service-level isolation
- Consistent naming conventions
AWS CodeBuild
The CodeBuild project handles running Ansible
version: 0.2
run-as: root
phases:
pre_build:
commands:
- apk list -i
build:
commands:
- ansible-playbook ansible/playbook.yamlDockerfile
The below dockerfile may not look too pretty, but it's optimized for performance. Using alpine is a minimal image, so it'll keep the size down. Having the commands all in one RUN command will mean less layers, which will also reduce the image size. Using Hadolint here helped understand best practices
FROM alpine:latest
RUN apk add --no-cache ansible=7.5.0-r0 aws-cli=2.13.5-r0 jq=1.6-r3 wget=1.21.4-r0 git=2.40.1-r0 python3 py3-pip && pip3 install --no-cache-dir botocore==1.31.22 boto3==1.28.22
AWS CloudFormation
Central Account Template
Description: |
The ConfigurationManagement CodeBuild Project Cloudformation Template
Parameters:
CostCenter:
Type: String
CodeBuildProjectName:
Type: String
Resources:
CodeBuildProject:
Type: AWS::CodeBuild::Project
Properties:
Description: ConfigurationManagement
Name: Ref: CodeBuildProjectName
Source:
Type: GITHUB
Location: https://github.com/<org-name>/configuration-management.git
GitCloneDepth: 0
BuildSpec: codebuild/buildspec.yaml
Triggers:
Webhook: true
FilterGroups:
- - Type: "EVENT"
Pattern: "PUSH"
- - Type: "HEAD_REF"
Pattern: "^refs/heads/main"
- - Type: "FILE_PATH"
Pattern: "READ_ME"
ExcludeMatchedPattern: true
Artifacts:
Type: NO_ARTIFACTS
LogsConfig:
CloudWatchLogs:
GroupName: ConfigurationManagement
Status: ENABLED
StreamName: ConfigurationManagement
ServiceRole: Ref: ServiceRole
Environment:
ComputeType: BUILD_GENERAL1_SMALL
Image: <SSAccountNumber>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com/configuration-management:latest
PrivilegedMode: true
Type: LINUX_CONTAINER
EnvironmentVariables:
- Name: CostCenter
Type: PLAINTEXT
Value: Ref: CostCenter
TimeoutInMinutes: 15
Tags:
- Key: "CostCenter"
Value: Ref: CostCenter
ServiceRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: ALLOW
Principal:
Service:
- codebuild.amazonaws.com
Action:
- 'sts:AssumeRole'
Path: /
Policies:
- PolicyName: ConfigManagementServicePolicy
PolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- 'sts:AssumeRole'
Resource:
- 'arn:aws:iam::<Account1>:role/ConfigurationManagementRole' #Dev
- 'arn:aws:iam::<Account2>:role/ConfigurationManagementRole' #Dev1
- 'arn:aws:iam::<Account3>:role/ConfigurationManagementRole' #Dev2
- 'arn:aws:iam::<Account4>:role/ConfigurationManagementRole' #CI
- 'arn:aws:iam::<Account5>:role/ConfigurationManagementRole' #UAT
- 'arn:aws:iam::<Account6>:role/ConfigurationManagementRole' #CustSand
- 'arn:aws:iam::<Account7>:role/ConfigurationManagementRole' #Stage
- 'arn:aws:iam::<Account8>:role/ConfigurationManagementRole' #Prod
- PolicyName:
Fn::Sub: ${CodeBuildProjectName}-codebuild-base-policy
PolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Resource:
- Fn::Sub: arn:aws:logs:${AWS::Region}:${AWS::AccountId}:log-group:${CodeBuildProjectName}
- Fn::Sub: arn:aws:logs:${AWS::Region}:${AWS::AccountId}:log-group:${CodeBuildProjectName}:*
Action:
- logs:CreateLogGroup
- logs:CreateLogStream
- logs:PutLogEvents
- Effect: Allow
Resource:
- Fn::Sub: arn:aws:s3:::codepipeline-${AWS::Region}-*
Action:
- s3:PutObject
- s3:GetObject
- s3:GetObjectVersion
- s3:GetBucketAcl
- s3:GetBucketLocation
NOTE: Because of Trust Policy requirements, the central stack needs to exist before deploying the StackSet below as the trust policy needs the central role to exist before deploying
Target Account Template (StackSet):
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: IAM role for configuration management with SSM full access and an EC2/SSM trust policy.
Resources:
ConfigurationManagementRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
RoleName: ConfigurationManagementRole
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS:
- arn:aws:iam::<shared-services-account>:role/ConfigurationManagementRole
Action: sts:AssumeRole
Policies:
- PolicyName: ConfigurationManagementPolicy
PolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- ssm:*
Resource: "*"Ansible
The ansible on this project could be summarized by essentially:
- Get the files that have changed in the commit that's triggering this build.
--- - hosts: localhost tasks: - name: Get last files changed shell: | last_2_commits=$(git log --format="%H" -n 2 | xargs) git diff --name-only $last_2_commits register: last_files - name: Get last Author Name shell: git log -n 1 '--pretty=%aN' register: last_author - Loop over these files one by one and execute the config management role. These files will represent an environment each
- name: Looping over configuration management role include_role: name: config_management with_items: "{{ last_files.stdout_lines }}" loop_control: loop_var: files_iterator when: '"Environment" in files_iterator' vars: changed_file: "{{ files_iterator.split('/').1 }}" - The start of the role assumes an AWS Role in the target account using:
# Assume role in target account and store credentials in session_token.sts_creds - name: Get AWS Session Credentials import_tasks: getToken.yaml- name: Get Access Token sts_assume_role: region: "{{ region }}" role_arn: "arn:aws:iam::{{ assume_role_account }}:role/ConfigurationManagementRole" role_session_name: "AnsibleSession" duration_seconds : "{{ assume_role_duration }}" register: session_token - It then loads the configuration from source, gets the values in the target account ssm parameter store and compares the two. The differences are registered in a variable called "diff_details"
# Get the configuration stored in GIT for this environment - name: Include GIT Configuration include_vars: "../Environments/{{ changed_file }}" # Get SSM Param Values From Target Account and return "" if not found - set_fact: output_item: "{{ lookup('aws_ssm', '{{item.value.name}}', region=region, aws_access_key=session_token.sts_creds.access_key, aws_secret_key=session_token.sts_creds.secret_key, aws_security_token=session_token.sts_creds.session_token, on_missing='skip') | default(None) }}" with_dict: "{{ ConfigurationValues}}" register: output_results # Sanitize output into a dictionary with just name, value and path - set_fact: remote_values: "{{ output_results.results | json_query('[*].{name: item.key, value: ansible_facts.output_item, path: item.value.name}') }}" # Get list of SSM Values differing from GIT - name: Diff Local And SSM ansible.utils.fact_diff: after: "{{ item.value.value }}" before: "{{ (remote_values | selectattr('path', 'search', item.value.name) | list | first).value }}" with_dict: - "{{ ConfigurationValues }}" register: diff_details - We then loop over the diff_details and update ssm parameter store in the target account
# Loop over the diff results and only action ones that changed For JSon Params - name: Update SSM Params JSON community.aws.ssm_parameter: state: present name: "{{ ConfigurationValues[diff_results.item.key].name }}" tier: "{{ ConfigurationValues[diff_results.item.key].tier }}" value: "{{ ConfigurationValues[diff_results.item.key].value | to_nice_json}}" string_type: "{{ ConfigurationValues[diff_results.item.key].type }}" description: "MANAGED BY ANSIBLE" aws_secret_key: "{{ session_token.sts_creds.secret_key }}" aws_access_key: "{{ session_token.sts_creds.access_key }}" session_token: "{{ session_token.sts_creds.session_token }}" region: "{{ region }}" with_items: "{{ diff_details.results }}" loop_control: loop_var: diff_results when: 'diff_results.changed == true and ConfigurationValues[diff_results.item.key].format == "json"' - The last step is then to send a slack notification of the change:
# Loop over the diff results and only action send notifications for the ones that changed - name: Send Notification include_tasks: send_notification.yaml with_items: "{{ diff_details.results }}" loop_control: loop_var: diff_results when: 'diff_results.changed == true'send_notification.yaml
- include_vars: slack_template.yaml # For debugging purposes display notify body - debug: msg="{{ notify_body }}" - debug: msg="{{ slack_payload }}" - name: Notify | Slack uri: url: "{{ slack_webhook }}" body: "{{ slack_payload }}" body_format: json method: POST register: slack_response - debug: msg="{{ slack_response }}"slack_template.yaml
slack_payload: text: "Configuration change enacted in {{ changed_file }} for {{ diff_results.item.key }}" username: "Configuration Management Ansible" title: "{{ changed_file }} Ansible Configuration Management {{ diff_results.item.key }}" colour: "good" fields: - title: "Environment" value: "{{ changed_file }}" short: true - title: "Service" value: "{{ diff_results.item.key }}" short: true - title: "GitCommit" value: "https://github.com/<organization>/configuration-management/commit/{{ commit_id }}" short: true - title: "Triggered By" value: "{{ last_author.stdout }}" short: true - title: "Diff Summary" value: "{{ diff_results.diff.prepared}}" short: false
ConfigurationExample
ConfigurationValues:
my_service1:
key_1: value_1
key_2: value_2
my_service2:
key_1: value_1
key_2: value_2Example project structure
.
├── ansible
│ ├── getToken.yaml
│ ├── group_vars
│ │ └── all.yaml
│ ├── playbook.yaml
│ ├── send_notification.yaml
│ ├── slack_template.yaml
│ ├── configuration_management
│ │ ├── defaults
│ │ │ └── main.yml
│ │ ├── handlers
│ │ │ └── main.yml
│ │ ├── meta
│ │ │ └── main.yml
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ ├── tasks
│ │ │ └── main.yml
│ │ ├── tests
│ │ │ ├── inventory
│ │ │ └── test.yml
│ │ └── vars
│ │ └── main.yml
│ └── teams_template.yaml
├── cloudformation.yaml
├── codebuild
│ └── buildspec.yaml
├── Dockerfile
├── Environments
│ ├── <company>-ci
│ ├── <company>-dev
│ ├── <company>-prod
│ ├── <company>-stage
│ ├── <company>-test
│ └── <company>-uat
└── README.mdResults and Impact
Business Value
- Faster feature delivery through efficient configuration management
- Reduced operational overhead and manual errors
- Improved configuration quality by replacing manual updates with automation
- Improved compliance through automated audit trails
Architectural Decisions
- Ansible was chosen for it's declarative approach to managing ssm configuration. The logic could have been implemented imperatively using boto3 but the in house ansible skills aloud for a faster turn around with declarative tools
- SSM Parameter store was already used for configuration in this particular setup. The main aim of the project was to efficiently manage changes to these ssm parameter store values via automation that could help audit configuration changes. On a greenfield project AWS CloudMap, DynamoDB or Hashicorp Vault could be good alternatives